Introduction to Agents
Learn how to build and use AI agents with tools, memory, and different agent types in FlowGenX
AI agents in FlowGenX are intelligent nodes within your workflow that can understand instructions, use tools to perform actions, and execute complex tasks autonomously.
Why Use Agents
Instead of hardcoding business logic, agents use AI reasoning to:
- Understand Context: Process inputs intelligently
- Use Tools: Call APIs, databases, and external services
- Remember Context: Maintain conversation history
- Adapt Dynamically: Handle edge cases without hardcoding
Core Components
Every agent is built from three essential pieces:
1. Large Language Model (LLM) - The "brain" (Claude, GPT-4, Groq, etc.)
2. Prompt - Instructions and personality. Define how the agent should behave.
3. Tools - Agent's ability to take action. Connect to APIs, databases, or external services.
Supporting: Memory enables agents to remember interactions. Input/Output Schema defines data flow.
Agent Types
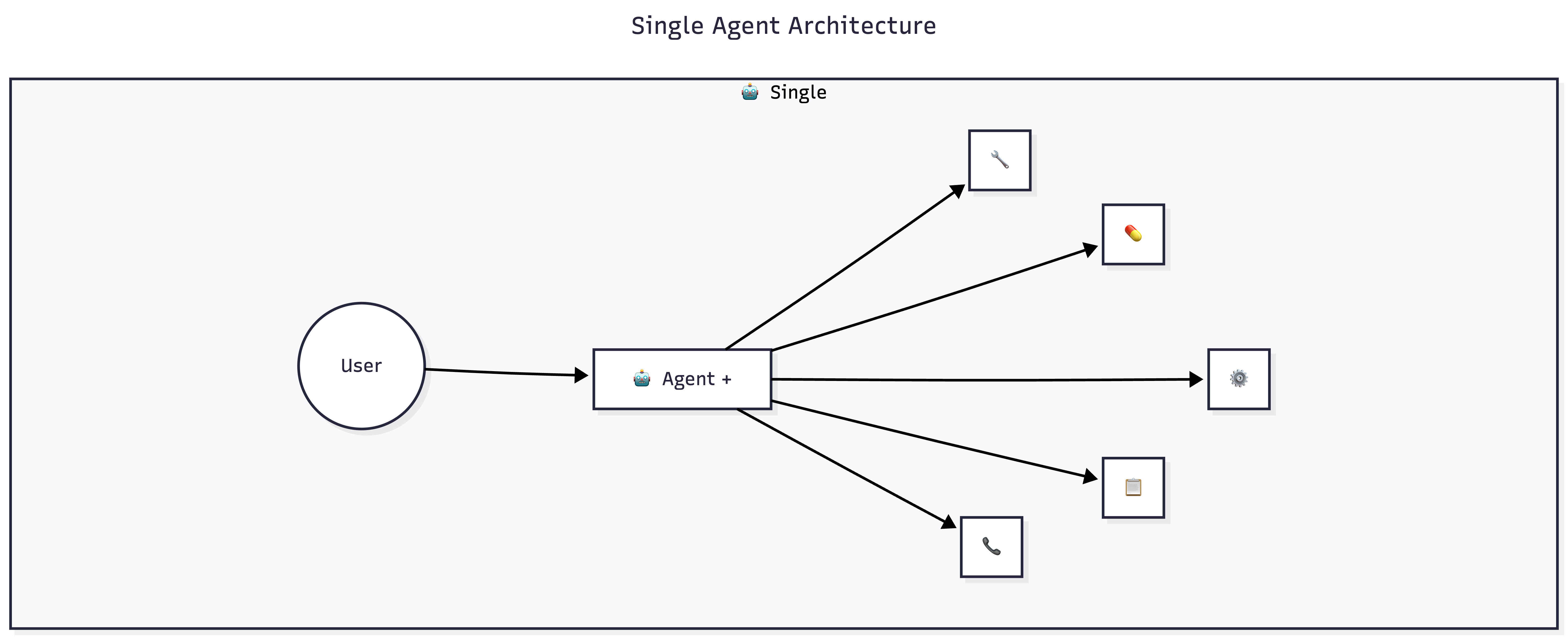
React Agents (Most Common)
- Analyze requests, think through steps, use tools, respond
- Best for: Support, analysis, decision-making
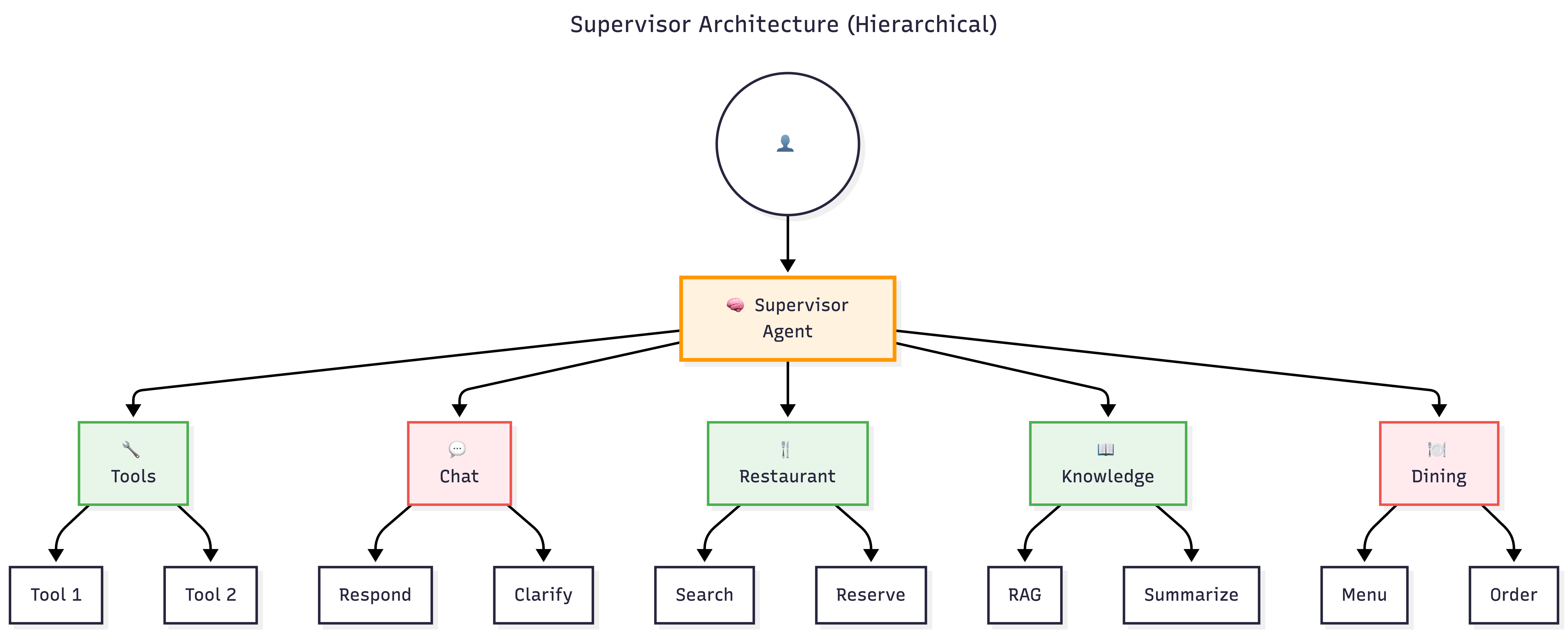
Supervisor Agents
- Coordinate multiple specialized agents
- Best for: Complex multi-step workflows
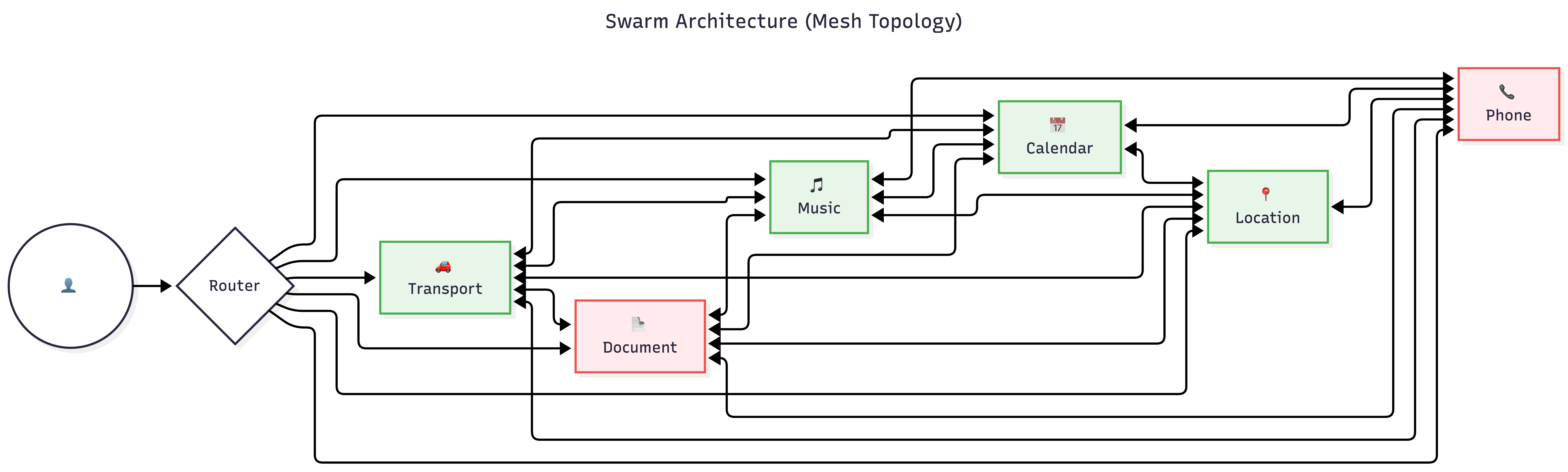
Swarm Agents
- Multiple agents working in parallel
- Best for: High-volume processing
How Agents Fit Into Workflows
Agents are nodes in your workflow canvas, just like data or logic nodes. They receive input from previous nodes, process with AI reasoning, use their tools as needed, and pass output to subsequent nodes.
Common Use Cases
- Customer Support: Handle inquiries, search knowledge base, respond
- Data Analysis: Query systems, generate insights, create reports
- Content Generation: Gather data, synthesize information, generate output
- Intelligent Routing: Analyze requests and route appropriately
- Automated Decisions: Evaluate data and make autonomous decisions