Python Tools
Create custom MCP tools with AI-assisted Python function generation
Python Tools allow you to create custom MCP tools by writing Python functions. With AI-assisted code generation, you can describe what you want in natural language and have Claude generate the implementation for you.
AI-Powered Tool Creation
Describe your tool in plain English and let AI generate the Python code
What Can Python Tools Do?
Python Tools are incredibly versatile. You can create tools that:
Data Processing
- Parse and transform data formats
- Calculate statistics and metrics
- Filter and aggregate datasets
Text Operations
- Extract information from text
- Format and template strings
- Validate input patterns
Calculations
- Mathematical computations
- Financial calculations
- Unit conversions
Business Logic
- Pricing calculations
- Eligibility checks
- Workflow decisions
Date & Time
- Date calculations
- Timezone conversions
- Schedule generation
Custom Integrations
- API wrapper functions
- Data validation logic
- Complex transformations
Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these steps to create a Python function tool:
Step 1: Select Python Function
1
Choose Python Function Tool Type
Open an existing MCP server (or create one using MCP Composer). Click Create New Tool and select "Python Function" to open the AI-assisted Python editor.
Step 2: Use AI to Generate Your Tool
2
Describe Your Tool to the AI Agent
The Python editor includes an embedded AI agent. Describe what you want in natural language, and the AI will generate:
- Complete Python function implementation with type hints
- Auto-generated input and output schemas
- Input validation and error handling
- Docstrings and inline documentation
Example prompt:"Create a function that calculates compound interest. It should take principal amount, annual interest rate, number of years, and compounding frequency as inputs."
You can iterate with the AI agent to refine the code, add features, or fix issues. The agent understands context and can make targeted improvements to your function.
Step 3: Configure Environment Variables (Optional)
3
Add Environment Variables
If your Python function needs API keys, tokens, or configuration values, add environment variables that your code can access at runtime.
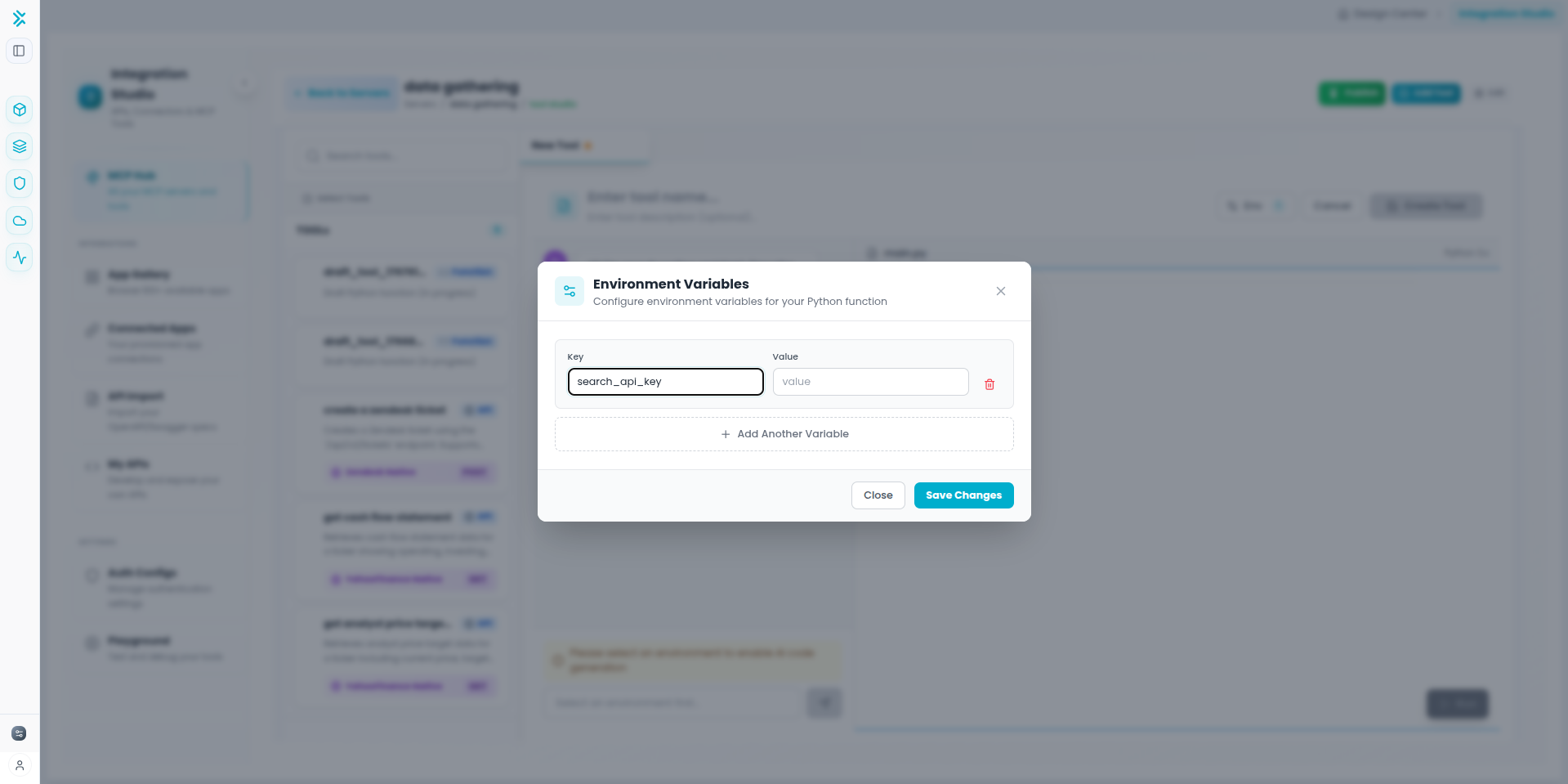
Security: Environment variables are stored securely and injected at runtime. Use them for sensitive data like API keys instead of hardcoding in your Python function.
Step 4: Test and Publish
4
Test and Make Available
Before publishing, test your function thoroughly:
- Use the built-in test interface with sample inputs
- Verify the output matches expectations
- Test edge cases (empty values, null, large numbers, etc.)
- Click Save when satisfied with the results
- Set status to Published to make available to agents
AI-Powered Features
Natural Language Input
Describe your tool in plain English—no Python expertise required to get started.
Conversational Refinement
Iterate with the AI to add features, fix bugs, or optimize your code.
Automatic Schema Generation
Input/output schemas are generated from your function signature—fully editable.
Context-Aware Assistance
The AI understands your server context and can create tools that integrate with your API endpoints.
Example AI Prompts
Effective Prompts for the AI Agent
Data Validation
"Validate email addresses and return validity status, domain, and username."
Date Calculation
"Calculate business days between two dates, excluding weekends and holidays."
Text Processing
"Extract and standardize phone numbers from text strings."
Financial Logic
"Calculate monthly loan payments from principal, interest rate, and term."
Pro Tip: Be specific about inputs, outputs, and edge cases. The more detail you provide, the better the generated code will be.
Best Practices
Building Effective Python Tools
Working with the AI Agent
- Be specific and detailed in your descriptions
- Explicitly request validation and error handling
- Ask for edge case handling upfront
- Iterate conversationally to refine the code
Tool Design
- Keep each function focused on one task
- Use descriptive names for tools and parameters
- Write clear descriptions for agent understanding
- Document return values and their meanings
Testing: Always test with edge cases—empty values, null inputs, extreme numbers, and invalid data types before publishing.