HTTP Request Node
Make REST API calls to external endpoints with OpenAPI integration
The HTTP Request node enables you to make REST API calls to external endpoints with full OpenAPI specification support, intelligent parameter management, and built-in testing capabilities.
Enterprise-Grade API Integration
OpenAPI-powered requests with intelligent autocomplete and testing
Overview
The HTTP Request node is your gateway to external APIs and services. Whether you're integrating with third-party platforms, calling internal microservices, or building complex API orchestrations, this node provides the enterprise features you need.
Key Capabilities
OpenAPI Integration
Select from registered OpenAPI specifications with automatic endpoint discovery and parameter extraction.
Smart Parameter Management
Autocomplete suggestions for headers, automatic path variable extraction, and expression field support.
Built-in Testing
Execute requests directly from the configuration UI, view responses, and debug before deployment.
Authentication Support
Endpoint-level authentication with OAuth, API keys, bearer tokens, and custom auth schemes.
Use Cases
- API Integrations: Connect to third-party SaaS platforms (Salesforce, Stripe, Twilio)
- Microservices: Call internal services and coordinate distributed operations
- Data Fetching: Retrieve data from REST APIs for processing in workflows
- Webhooks: Send notifications and updates to external systems
- External Actions: Trigger operations in connected systems
Configuration Guide
1. API Integration
The first step is selecting your API and endpoint from registered OpenAPI specifications.
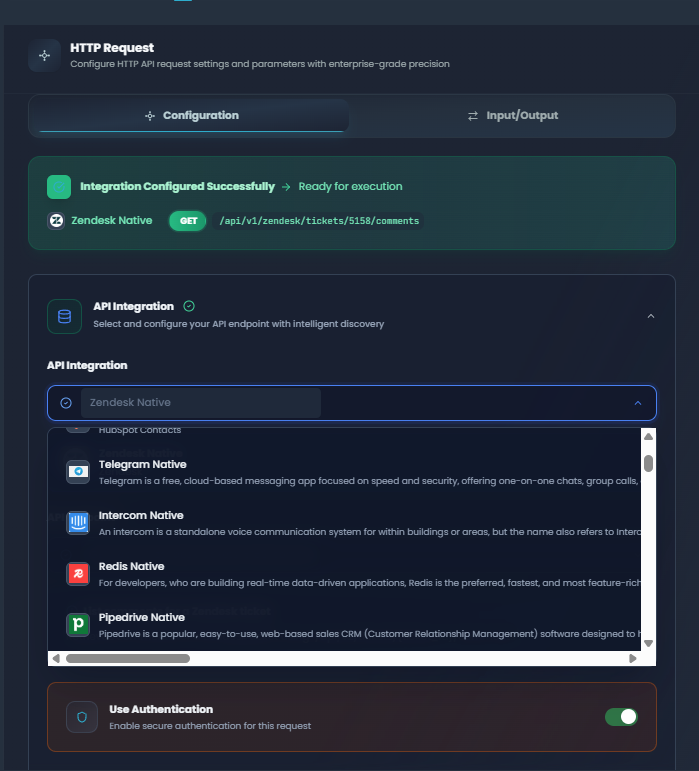
API Integration section showing API selection, endpoint dropdown, and authentication toggle
Steps to configure:
-
Select API: Click the API dropdown and choose from your registered OpenAPI specifications
- APIs must be pre-registered in your environment
- Each API represents an external service or internal microservice
-
Choose Endpoint: After selecting an API, pick the specific endpoint you want to call
- Endpoints are automatically discovered from the OpenAPI spec
- Method (GET/POST/PUT/PATCH/DELETE) and path are displayed
- Endpoint summary and description are shown when available
-
Authentication Toggle: Enable authentication if the endpoint requires it
- Authentication configuration is pulled from the endpoint specification
- Supports OAuth, API keys, bearer tokens, and custom schemes
- Credentials are managed securely at the environment level
Once configured, you'll see a success banner confirming the integration is ready.
2. Request Parameters
Configure query parameters, headers, and path variables using the tabbed interface.
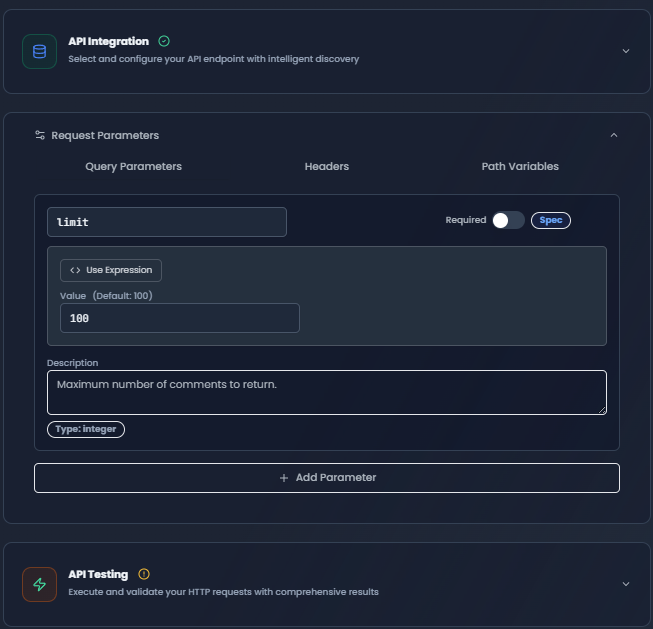
Request Parameters with Query Parameters tab active showing configured parameters
Query Parameters
Add URL query parameters that will be appended to the request URL.
Configuration:
- Parameter Name: The query parameter key (e.g.,
page,limit,filter) - Value: The parameter value (supports expressions)
- Description: Optional documentation for the parameter
- Required Toggle: Mark if the parameter is required
Expression Support:
- Use
{{upstream.node_name.output_field}}to reference previous node outputs - Use
{{global.variable_name}}for global variables - Combine static and dynamic values:
filter={{upstream.filter_node.value}}
Source Badges:
- Spec: Automatically extracted from OpenAPI specification
- Saved: Previously saved configuration
- Manual: Added manually by user
- Suggested: Default values from specification
Headers
Configure HTTP headers with intelligent autocomplete suggestions.
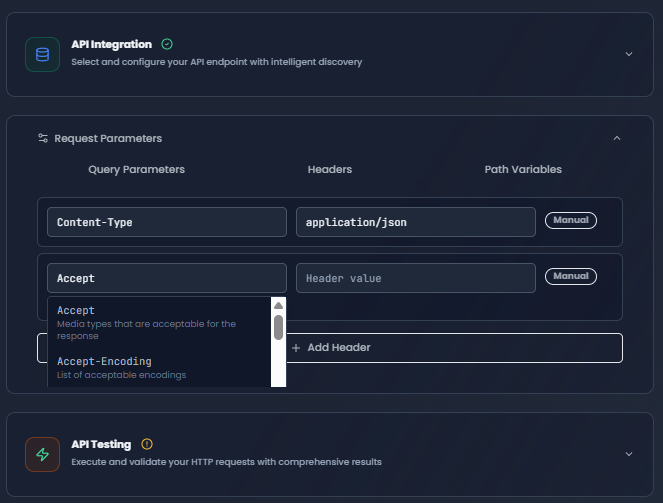
Headers tab with autocomplete dropdown showing Content-Type, Accept, and Authorization suggestions
Common Headers (Autocomplete Available):
| Header | Purpose | Common Values |
|---|---|---|
Content-Type | Request body format | application/json, application/xml, multipart/form-data |
Accept | Response format preference | application/json, application/xml, */* |
Authorization | Authentication | Bearer {token}, Basic {credentials} |
User-Agent | Client identification | FlowGenX/1.0 |
Accept-Encoding | Compression support | gzip, deflate, br |
Custom Headers:
- Add any custom headers required by your API
- Use expressions for dynamic values
- Source badges indicate where the header came from
Path Variables
Path variables are automatically extracted from the endpoint path and marked as required.
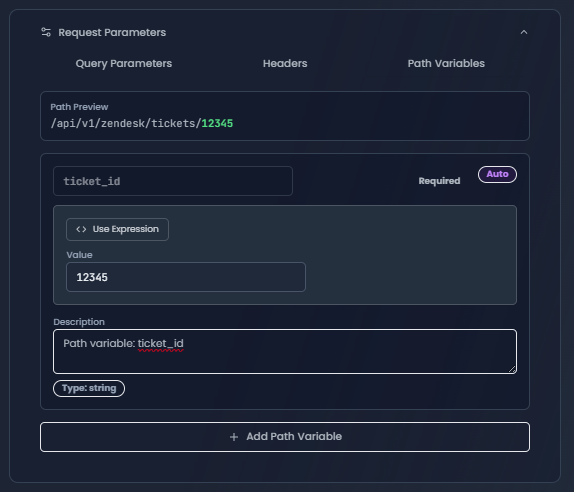
Path Variables tab showing auto-extracted required variables with validation
How Path Variables Work:
For an endpoint like /api/users/{userId}/orders/{orderId}, the system automatically:
- Extracts
userIdandorderIdas path variables - Marks them as required
- Shows a path preview with highlighted variables
- Validates that all variables have values before execution
Path Preview:
- Shows the complete path with variables in different colors
- Green indicates variables with values assigned
- Orange indicates missing required variables
- Hover for variable descriptions
3. Request Body
Configure the JSON request body for POST, PUT, and PATCH requests.
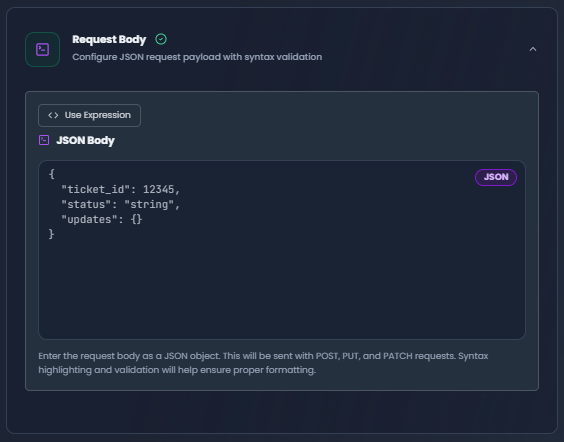
Request Body editor with JSON syntax highlighting and expression field support
Body Editor Features:
- Syntax Highlighting: JSON is formatted and highlighted for readability
- Expression Integration: Switch between manual and expression modes
- Template Suggestions: Use placeholder examples as starting points
- Validation: Real-time JSON validation with error indicators
Example Body:
{
"customer": {
"id": "{{upstream.customer_node.customer_id}}",
"email": "{{upstream.customer_node.email}}",
"name": "{{upstream.customer_node.full_name}}"
},
"order": {
"items": "{{upstream.cart_node.items}}",
"total": "{{upstream.cart_node.total_amount}}",
"currency": "USD"
},
"metadata": {
"source": "workflow",
"workflow_id": "{{global.workflow_id}}",
"timestamp": "{{global.current_timestamp}}"
}
}Expression Patterns:
- Reference upstream outputs:
{{upstream.node_name.field}} - Use global variables:
{{global.variable_name}} - Mix static and dynamic:
"status": "pending"alongside expressions
4. Test Execution
Test your HTTP request configuration before deploying to production.
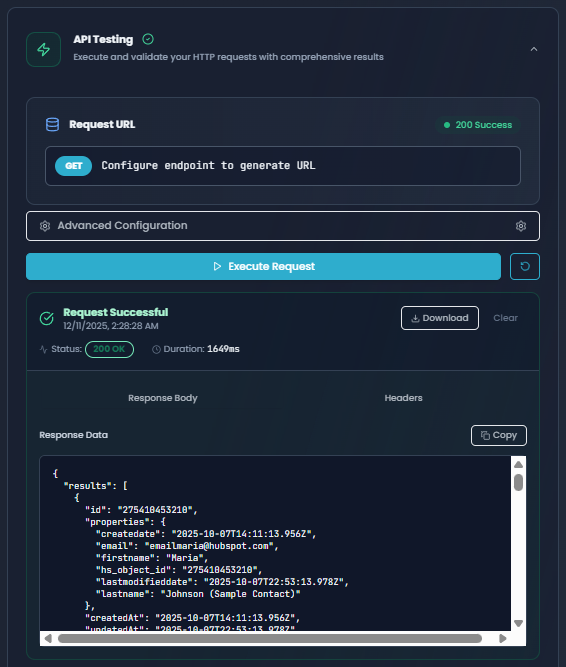
Test Execution section showing successful request with status code, response body, and headers
Testing Features:
-
URL Preview: See the complete request URL with all parameters substituted
-
Execute Button: Click to send the request to the actual endpoint
-
Advanced Configuration:
- Custom URL Override: Test against different environments
- Custom Body Override: Try different payloads
-
Response Display:
- Body Tab: View the JSON response data
- Headers Tab: Inspect response headers
- Status Indicator: Shows HTTP status code (200, 404, 500, etc.)
- Duration: Request execution time in milliseconds
-
Actions:
- Copy response to clipboard
- Download response as JSON file
- Clear results
Reading Test Results:
| Status Code | Meaning | Next Steps |
|---|---|---|
| 200-299 | Success | Configuration is correct, ready for production |
| 400-499 | Client Error | Check parameters, headers, or authentication |
| 500-599 | Server Error | External API issue, check API status |
| 0 | Network Error | Check connectivity, URL, or timeout settings |
Using Expression Fields
Expression fields enable dynamic value binding from upstream nodes, global variables, and workflow state.
Expression Syntax
FlowGenX uses JEXL expressions wrapped in {{ }} with support for 40+ transforms.
// Reference upstream node output (bracket notation)
{{ ["node-id"].outputData[0].field_name }}
{{ ["customer-node"].params.customer_id }}
// Reference upstream node output (sanitized format)
{{ node_customer_node.outputData[0].email }}
{{ node_data_processor.params.threshold }}
// Access global variables (vars namespace)
{{ vars.tenant_id }}
{{ vars.environment_id }}
{{ vars.authToken }}
// Current node reference
{{ $.params.api_key }}
{{ $.inputData[0].customer_id }}
// Direct field access (from current node input)
{{ customer_email }}
{{ order_total }}
// Nested object access
{{ node_customer_node.outputData[0].address.city }}
{{ ["customer-node"].params.config.database.host }}
// Array indexing
{{ node_items_node.outputData[0].results[0].id }}
{{ $.inputData[0].items[0].price }}
// Using transforms
{{ customer_email | lower }}
{{ order_total | toNumber | round(2) }}
{{ description | trim | slice(0, 100) }}Common Expression Patterns
1. Customer Data Flow:
{
"customer_id": "{{ node_get_customer.outputData[0].id }}",
"email": "{{ node_get_customer.outputData[0].email | lower }}",
"full_name": "{{ node_get_customer.outputData[0].first_name | concat(' ', node_get_customer.outputData[0].last_name) }}",
"preferences": "{{ ["get-customer"].outputData[0].preferences | toJson }}"
}2. Conditional Values with Transforms:
// Using if() function for conditional logic
"status": "{{ if(node_validator.outputData[0].is_valid, 'approved', 'pending') }}"
// With type conversion and rounding
"discount": "{{ if(order_total > 1000, order_total * 0.1, 0) | round(2) }}"
// Conditional with transform chain
"priority": "{{ if(severity | upper == 'CRITICAL', 1, 5) }}"3. Global Variables and Workflow Context:
{
"tenant_id": "{{ vars.tenant_id }}",
"environment": "{{ vars.environment_id }}",
"user_email": "{{ vars.current_user_email | lower }}",
"workflow_id": "{{ vars.workflow_id }}",
"timestamp": "{{ now('YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss') }}",
"execution_id": "{{ vars.execution_id }}"
}4. Chaining Requests (Sequential Node Outputs):
{
"user_id": "{{ node_create_user.outputData[0].id }}",
"session_token": "{{ node_authenticate.outputData[0].token }}",
"resource_id": "{{ node_create_resource.outputData[0].resource_id }}",
"permissions": "{{ ["create-user"].outputData[0].permissions | toJson }}"
}5. Transform Chains for Data Processing:
// Email normalization
"email": "{{ customer_email | trim | lower }}"
// Price calculation with rounding
"total": "{{ (subtotal + tax) | toNumber | round(2) }}"
// Array operations
"tags": "{{ tag_string | split(',') | unique | join(', ') }}"
// String truncation
"summary": "{{ description | trim | slice(0, 200) | concat('...') }}"Expression Reference
Quick Transform Reference
FlowGenX provides 40+ transforms for data manipulation. Here are the most commonly used in HTTP requests:
| Category | Transform | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| String | lower | {{ email | lower }} | "user@example.com" |
upper | {{ country | upper }} | "USA" | |
trim | {{ input | trim }} | "hello" | |
concat | {{ firstName | concat(' ', lastName) }} | "John Doe" | |
| Number | toNumber | {{ price | toNumber }} | 42.99 |
round | {{ value | round(2) }} | 3.14 | |
| Array | join | {{ tags | join(', ') }} | "a, b, c" |
length | {{ items | length }} | 5 | |
first | {{ array | first }} | First element | |
sum | {{ prices | sum }} | 150.50 | |
| Type | toJson | {{ object | toJson }} | JSON string |
parseJson | {{ jsonStr | parseJson }} | Parsed object | |
| Date | now | {{ now('YYYY-MM-DD') }} | "2024-03-15" |
date | {{ timestamp | date('MM/DD/YYYY') }} | "03/15/2024" | |
| Logic | if() | {{ if(age >= 18, 'adult', 'minor') }} | Conditional value |
Available Expression Contexts
When building expressions in HTTP Request node, you have access to:
-
Upstream Nodes - Access output from previous nodes
{{ node_previous_node.outputData[0].field_name }} {{ ["previous-node"].params.setting }} -
Global Variables - Access exported workflow variables
{{ vars.authToken }} {{ vars.tenant_id }} -
Current Node - Reference current node parameters
{{ $.params.api_key }} {{ $.params.base_url }} -
Direct Fields - Quick access to input fields
{{ customer_email }} {{ order_id }}
Expression Best Practices for HTTP Requests
Headers:
- Always use
{{ vars.authToken }}for authentication tokens - Normalize emails:
{{ email | lower | trim }} - Generate unique IDs:
{{ vars.execution_id }}
Request Body:
- Round numeric values:
{{ price | toNumber | round(2) }} - Combine strings safely:
{{ firstName | concat(' ', lastName) }} - Handle nested objects:
{{ ["node-id"].outputData[0].nested.field }}
Query Parameters:
- Convert to proper types:
{{ pageSize | toInteger }} - Conditional parameters:
{{ if(includeArchived, 'true', 'false') }}
Path Variables:
- Always use required fields:
{{ node_source.outputData[0].id }} - Sanitize values:
{{ customerId | toString | trim }}
Complete Expression Documentation
For comprehensive expression documentation including:
- Full list of 40+ transforms with examples
- Context structure for batch and event-driven workflows
- Advanced expression patterns and recipes
- TypeScript type definitions
- Best practices and troubleshooting
See the complete Expression System Reference Guide in the FlowGenX repository.
Complete Configuration Example
Here's a real-world example of creating a customer order in an e-commerce API.
Scenario
You need to create an order after collecting customer information and cart items from previous workflow nodes.
Full Configuration
{
"node_type": "http_request",
"node_id": "create_order_001",
"config": {
// API Integration
"open_api_id": "ecommerce-api-v2",
"endpoint_id": "endpoint_create_order_post",
"use_authentication": true,
// Request Configuration
"method": "POST",
"path": "/api/v2/orders",
// Query Parameters
"parameters": {
"idempotency_key": {
"value": "{{ vars.workflow_execution_id }}",
"description": "Prevent duplicate orders",
"source": "manual"
},
"send_confirmation": {
"value": "true",
"description": "Send email confirmation",
"source": "manual"
},
"customer_tier": {
"value": "{{ if(order_count | toNumber > 10, 'premium', 'standard') }}",
"description": "Customer tier based on order history",
"source": "manual"
}
},
// Headers
"headers": {
"Content-Type": {
"value": "application/json",
"description": "JSON request body",
"source": "spec"
},
"Authorization": {
"value": "Bearer {{ vars.authToken }}",
"description": "API authentication token",
"source": "manual"
},
"X-Client-Version": {
"value": "FlowGenX/1.0",
"description": "Client identifier",
"source": "manual"
},
"X-Request-ID": {
"value": "{{ vars.execution_id }}",
"description": "Unique request identifier",
"source": "manual"
}
},
// Path Variables (if path was /api/v2/customers/{customerId}/orders)
"pathVariables": {
"customerId": {
"value": "{{ node_get_customer.outputData[0].id }}",
"required": true
}
},
// Request Body
"body": {
"customer": {
"id": "{{ node_get_customer.outputData[0].customer_id }}",
"email": "{{ node_get_customer.outputData[0].email | lower | trim }}",
"name": "{{ node_get_customer.outputData[0].first_name | concat(' ', node_get_customer.outputData[0].last_name) | title }}",
"shipping_address": {
"street": "{{ ["get-customer"].outputData[0].address.street }}",
"city": "{{ ["get-customer"].outputData[0].address.city | title }}",
"postal_code": "{{ ["get-customer"].outputData[0].address.postal_code }}",
"country": "{{ ["get-customer"].outputData[0].address.country | upper }}"
}
},
"items": "{{ node_cart.outputData[0].items }}",
"totals": {
"subtotal": "{{ node_cart.outputData[0].subtotal | toNumber | round(2) }}",
"tax": "{{ node_cart.outputData[0].tax | toNumber | round(2) }}",
"shipping": "{{ node_cart.outputData[0].shipping | toNumber | round(2) }}",
"total": "{{ (node_cart.outputData[0].subtotal + node_cart.outputData[0].tax + node_cart.outputData[0].shipping) | toNumber | round(2) }}",
"currency": "USD"
},
"payment": {
"method": "card",
"token": "{{ node_payment_processor.outputData[0].token }}",
"last4": "{{ node_payment_processor.outputData[0].card_last4 }}"
},
"metadata": {
"source": "workflow",
"workflow_id": "{{ vars.workflow_id }}",
"workflow_name": "{{ vars.workflow_name }}",
"tenant_id": "{{ vars.tenant_id }}",
"created_by": "{{ vars.current_user_email }}",
"timestamp": "{{ now('YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss') }}",
"order_count": "{{ order_count | toInteger }}"
}
}
},
// Output Mapping
"outputs": {
"order_id": "$.id",
"order_number": "$.order_number",
"status": "$.status",
"confirmation_url": "$.confirmation_url"
}
}Expected Response
{
"id": "ord_1234567890",
"order_number": "ORD-2024-001234",
"status": "confirmed",
"confirmation_url": "https://store.example.com/orders/ord_1234567890",
"created_at": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z",
"customer": {
"id": "cus_987654321",
"email": "customer@example.com"
},
"totals": {
"currency": "USD",
"total": 156.99
}
}Authentication
Authentication is managed at the endpoint level and automatically applied when enabled.
Supported Authentication Types
| Type | Configuration | Example |
|---|---|---|
| OAuth 2.0 | Client credentials, authorization code | Bearer token auto-refreshed |
| API Key | Header, query parameter, or custom location | X-API-Key: {key} |
| Bearer Token | JWT or opaque tokens in Authorization header | Authorization: Bearer {token} |
| Basic Auth | Username and password encoded | Authorization: Basic {base64} |
| Custom | Custom headers and logic | Signature-based auth |
Authentication Flow
- Configuration: Auth settings are stored with the endpoint in the OpenAPI spec
- Credential Storage: Actual credentials are stored securely at the environment level
- Automatic Injection: When authentication is enabled, credentials are automatically injected
- Token Refresh: OAuth tokens are automatically refreshed before expiration
- Error Handling: 401/403 responses trigger re-authentication if configured
Security Best Practices
Security Recommendations
- • Never hardcode API keys or tokens in the configuration
- • Use environment-level credential storage
- • Rotate credentials regularly
- • Use the minimum required authentication scope
- • Enable authentication for production endpoints
- • Test authentication in a non-production environment first
Error Handling
The HTTP Request node provides comprehensive error handling and reporting.
Error Structure
When a request fails, the node outputs an error object:
{
"success": false,
"status": 400,
"statusText": "Bad Request",
"error": "Validation failed",
"details": {
"field": "email",
"message": "Invalid email format"
},
"timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z",
"duration": 245
}Common Error Scenarios
| Error Type | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| 400 Bad Request | Invalid parameters or body | Check parameter values and JSON syntax |
| 401 Unauthorized | Missing or invalid authentication | Verify credentials and authentication config |
| 403 Forbidden | Insufficient permissions | Check API access level and scopes |
| 404 Not Found | Invalid endpoint or path variables | Verify URL and path variable values |
| 429 Too Many Requests | Rate limit exceeded | Implement retry with backoff |
| 500 Server Error | External API issue | Check API status, implement retry |
| Network Timeout | Request took too long | Increase timeout or optimize request |
Retry Configuration
Configure automatic retries for transient failures:
{
"retry": {
"enabled": true,
"max_attempts": 3,
"backoff_strategy": "exponential",
"retry_on_status": [429, 500, 502, 503, 504]
},
"timeout": 30000
}Best Practices
1. Endpoint Organization
- Use OpenAPI Specs: Register all APIs as OpenAPI specifications for auto-discovery
- Version APIs: Include version in the base URL or path (e.g.,
/api/v2/) - Document Endpoints: Add descriptions and summaries to help team members
2. Security Considerations
- Credential Management: Store credentials at the environment level, never in configs
- HTTPS Only: Always use HTTPS endpoints in production
- Input Validation: Validate upstream data before using in requests
- Rate Limiting: Implement proper rate limiting and backoff strategies
3. Performance Optimization
- Parallel Requests: Use parallel nodes for independent API calls
- Caching: Cache responses when appropriate to reduce API calls
- Timeouts: Set reasonable timeouts (30s default, adjust based on API)
- Batch Operations: Use batch endpoints when processing multiple items
4. Testing Recommendations
- Test Early: Use the built-in test execution during development
- Multiple Environments: Test against dev/staging before production
- Edge Cases: Test with empty values, large payloads, and error scenarios
- Monitor: Track request duration and error rates in production
Advanced Features
Custom URL Override
During testing or for dynamic endpoint selection:
{
"custom_url_override": "{{upstream.service_discovery.endpoint_url}}"
}Response Transformation
Transform API responses using output mapping:
{
"outputs": {
"user_id": "$.data.user.id",
"full_name": "$.data.user.firstName + ' ' + $.data.user.lastName",
"is_active": "$.data.user.status === 'active'"
}
}Conditional Execution
Combine with conditional nodes for smart API routing:
[Check Cache] → [If Not Cached] → [HTTP Request] → [Update Cache]
↓
[Return Cached Data]Rate Limiting Handling
Implement intelligent rate limit handling:
{
"on_rate_limit": {
"wait_for_reset": true,
"max_wait_seconds": 60,
"fallback": "use_cached_data"
}
}Integration Patterns
Pattern 1: Sequential API Calls
Chain multiple API calls where each depends on the previous:
[Create User] → [Create Profile] → [Send Welcome Email] → [Subscribe to Newsletter]Pattern 2: Parallel Data Fetching
Fetch data from multiple sources simultaneously:
[Parallel Split]
↓ ↓ ↓
[API 1] [API 2] [API 3]
↓ ↓ ↓
[Merge Results]Pattern 3: Error Recovery
Implement fallback logic for failed requests:
[Primary API] → [If Error] → [Fallback API] → [If Error] → [Use Default Data]
↓
[Success Path]Pattern 4: Batch Processing
Process items in batches with rate limiting:
[Get Items] → [Batch Split] → [For Each Batch] → [HTTP Request + Delay] → [Merge Results]Troubleshooting
Configuration Errors
| Issue | Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoint not loading | API not registered or network issue | Check API registration and connectivity |
| Path variables empty | Endpoint path doesn't contain {variables} | Verify endpoint path format in OpenAPI spec |
| JSON body invalid | Syntax error or expression issue | Use JSON validator, check expression syntax |
| Headers not applied | Expression not resolving | Test expressions, verify upstream node outputs |
Authentication Issues
- 401 Unauthorized: Check if authentication is enabled and credentials are valid
- 403 Forbidden: Verify API access level and permission scopes
- Token Expired: Check token refresh configuration for OAuth
- Invalid Credentials: Rotate credentials at the environment level
Network & Timeout Problems
- Connection Timeout: Check network connectivity and firewall rules
- Request Timeout: Increase timeout setting or optimize API performance
- DNS Resolution: Verify base URL and domain configuration
- SSL/TLS Errors: Check certificate validity and SSL configuration
JSON Parsing Errors
- Invalid JSON Body: Validate JSON syntax before sending
- Expression Not Resolving: Check upstream node outputs are available
- Type Mismatch: Ensure data types match API expectations
- Malformed Response: API returning non-JSON, check Content-Type
Next Steps
API Composer
Register and manage OpenAPI specifications
Working with Data
Expression syntax and data transformation
Logic Nodes
Add conditional logic and error handling
Complex Orchestration
Build advanced API workflows
Summary
The HTTP Request node is your gateway to external APIs with enterprise-grade features:
- OpenAPI Integration: Automatic endpoint discovery and configuration
- Smart Autocomplete: Intelligent suggestions for headers and parameters
- Expression Support: Dynamic value binding from workflow context
- Built-in Testing: Execute and debug requests before deployment
- Authentication: Secure credential management with multiple auth types
- Error Handling: Comprehensive error reporting and retry logic
Whether you're building simple integrations or complex multi-API orchestrations, the HTTP Request node provides the reliability and features you need for production workflows.