NLP Stream
Event-based NLP processing with smart code generation capabilities

The NLP Stream node provides event-based natural language processing capabilities within your workflows. This node enables real-time NLP processing with an integrated AI assistant for smart code generation, making it easy to build sophisticated language processing workflows without manual coding.
Why Use NLP Stream?
The NLP Stream is ideal when you need to:
- Process natural language events - Handle text processing tasks in real-time as events occur
- Generate NLP code with AI - Use the built-in AI assistant to generate processing logic
- Build language processing pipelines - Create workflows that analyze, transform, or understand text
- Configure schemas dynamically - Define input/output structures automatically or manually
- Stream text processing - Handle continuous text data processing workflows
- Leverage AI assistance - Get help creating NLP processing logic through conversational AI
How It Works
The NLP Stream node combines event-based processing with AI-assisted configuration:
- Event-Based Processing - Processes natural language data as events flow through the workflow
- Smart Code Generation - AI assistant helps generate processing logic based on your requirements
- Schema Management - Flexible input/output schema configuration (automatic or manual)
- Generation Tracking - Monitors the number of AI-generated configurations
- Conversational Interface - Natural language interaction with the AI assistant
When to Use NLP Stream
Use NLP Stream when:
- You need to process text data in response to events
- You want AI assistance in building NLP processing logic
- You're creating text analysis or transformation workflows
- You need flexible schema configuration for language data
- You want to leverage smart code generation for NLP tasks
- You're building conversational or language understanding workflows
Configuration
Setting up the NLP Stream node involves working with the AI assistant and configuring input/output schemas.
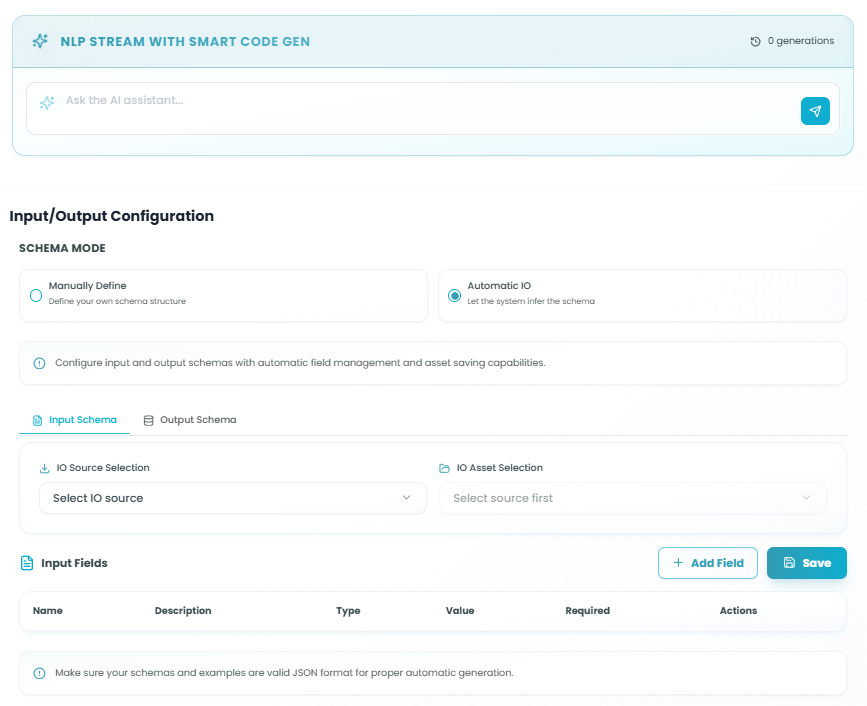
NLP Stream with Smart Code Gen
AI Assistant Interface:
The top section provides an AI-powered assistant to help you configure the NLP Stream node:
-
Ask the AI assistant... - Input field where you can describe what you want the NLP node to do
- Use natural language to explain your NLP processing requirements
- The AI will help generate appropriate configurations
- Examples: "Extract entities from customer feedback", "Analyze sentiment of social media posts"
-
Send Button - Submit your request to the AI assistant
- Click to get AI-generated suggestions and configurations
- The AI helps create the processing logic you need
-
Generations Counter - Shows how many AI generations have been created
- Displays "0 generations" initially
- Increments as you use the AI assistant
- Helps track AI assistance usage
How to Use the AI Assistant:
- Describe your NLP processing needs in natural language
- Click the send button to submit your request
- Review the AI-generated configuration suggestions
- Apply the suggestions to your node configuration
- Iterate with the AI to refine the processing logic
Input/Output Configuration
The Input/Output Configuration section allows you to define the data structure for your NLP processing.
Schema Mode:
Choose how you want to define your input and output schemas:
-
Manually Define - Define your own schema structure
- Full control over input and output fields
- Manually create field definitions
- Best for specific, custom data structures
-
Automatic IO - Let the system infer the schema
- Automatically generates schema from workflow context
- Saves time with intelligent field detection
- Best for standard NLP processing flows
Note: The configuration message states: "Configure input and output schemas with automatic field management and asset saving capabilities."
Input Schema Tab
The Input Schema tab allows you to define what data the NLP Stream node will receive.
IO Source Selection:
- Select IO source dropdown - Choose where input data comes from
- Import from upstream nodes
- Define custom input sources
- Connect to event sources
Input Fields:
Define the structure of incoming text data:
- Click Add Field to create input field definitions
- Configure each field with:
- Name - Field identifier
- Description - What the field contains
- Type - Data type (string, object, array, etc.)
- Value - Default value or expression
- Required - Whether the field is mandatory
- Actions - Edit or remove field
The table displays all configured input fields with columns for Name, Description, Type, Value, Required, and Actions.
Important Note: "Make sure your schemas and examples are valid JSON format for proper automatic generation."
Output Schema Tab
The Output Schema tab defines what processed data the NLP Stream node will produce.
IO Asset Selection:
- Select source first dropdown - Choose the output structure source
- Define based on processing requirements
- Automatically infer from NLP operations
- Specify custom output format
Output Fields:
Similar to input fields, define the structure of processed NLP results. The AI assistant can help determine appropriate output fields based on your NLP processing goals.
Using the NLP Stream in Your Workflow
After configuration:
- The NLP Stream node receives natural language data or events
- Processes the text according to your configured logic
- AI-generated or manually defined processing is applied
- Results are output in the defined schema structure
- Downstream nodes receive the processed NLP data
Processing Flow:
Text Event/Data → NLP Stream Node →
AI-Assisted Processing →
Structured Output → Downstream NodesBest Practices
AI Assistant Usage
- Be specific in requests - Clearly describe what you want the NLP processing to do
- Iterate with the AI - Refine your requests based on generated suggestions
- Verify generated code - Review AI suggestions before applying
- Use natural language - Describe processing needs conversationally
- Track generations - Monitor AI usage through the generation counter
Schema Configuration
- Choose appropriate mode - Use Automatic IO for standard flows, Manually Define for custom needs
- Validate JSON format - Ensure schemas are valid JSON for automatic generation
- Define clear inputs - Specify exactly what text data you expect
- Plan output structure - Design output schema to match downstream node requirements
- Use descriptive fields - Name fields clearly to indicate their purpose
NLP Processing
- Match input to event type - Configure inputs to handle expected text event structure
- Define processing goals - Be clear about what NLP operations you need
- Test with sample data - Verify processing works with representative text
- Handle edge cases - Consider empty strings, unusual formatting, etc.
- Monitor performance - Track processing speed for text data
Common Use Cases
Text Analysis:
- Sentiment analysis on customer feedback
- Entity extraction from documents
- Topic classification of content
- Language detection and translation
Event Processing:
- Real-time chat message analysis
- Social media post processing
- Customer support ticket categorization
- Content moderation and filtering
Data Transformation:
- Text normalization and cleaning
- Format conversion and standardization
- Information extraction and structuring
- Summary generation from long texts
Intelligent Processing:
- Intent recognition from user inputs
- Question answering systems
- Automated tagging and labeling
- Context-aware text processing
Troubleshooting
AI Assistant Not Responding:
- Check your network connection
- Verify the request is clear and specific
- Try rephrasing your request
- Review generation counter to ensure service is available
Schema Validation Errors:
- Ensure JSON format is valid
- Check all required fields are defined
- Verify field types are correct
- Review schema structure matches NLP processing needs
Processing Not Working:
- Verify input schema matches incoming data
- Check that AI-generated logic is applied
- Ensure output schema is properly configured
- Review upstream node connections
Performance Issues:
- Monitor the number of events being processed
- Check complexity of NLP operations
- Verify schema definitions are optimized
- Consider batch processing for large volumes
Monitoring NLP Stream
Monitor your NLP Stream node:
- Track generation usage - Monitor AI assistant invocations
- Review processing results - Verify NLP outputs are correct
- Check schema compliance - Ensure data matches defined schemas
- Monitor throughput - Track event processing rates
- Analyze errors - Review failures and adjust configuration
For more information on monitoring workflow executions, see the Traceability documentation.
Next Steps
After setting up your NLP Stream node:
- Describe your NLP processing needs to the AI assistant
- Review and apply AI-generated configuration suggestions
- Configure input schema to match your text event structure
- Define output schema for processed NLP results
- Test with sample text data
- Deploy and monitor NLP processing in production
The NLP Stream node brings powerful AI-assisted natural language processing to your FlowGenX workflows, making it easy to build sophisticated text processing pipelines with minimal manual configuration.