MCP Tool
Add individual Model Context Protocol tools to extend agent capabilities

The MCP Tool node allows you to add individual Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools to your workflows. These tools extend the capabilities of your agents by providing specialized functions they can invoke, such as web search, file operations, API calls, data extraction, and more. MCP tools follow a standardized protocol that enables agents to discover and use them intelligently.
Why Use MCP Tool?
The MCP Tool is ideal when you need to:
- Extend agent capabilities - Add specific functions that agents can use to accomplish tasks
- Integrate external services - Connect to APIs and external systems through standardized tools
- Provide specialized functions - Give agents access to domain-specific operations
- Enable tool usage - Allow agents to perform actions beyond language model capabilities
- Build custom integrations - Create workflows that combine AI reasoning with external tools
- Grant selective access - Choose specific tools for specific agents rather than entire server collections
How It Works
MCP Tools provide a standardized interface for agents to interact with external functions:
- Tool Registration - Tools are registered and made available to connected agents
- Agent Invocation - Agents can call tools based on their prompts and reasoning
- Parameter Passing - Agents provide appropriate parameters when invoking tools
- Result Processing - Tool outputs are returned to agents for further processing
- Context Awareness - Tools understand the context of the workflow and execution
When to Use MCP Tool
Use MCP Tool when:
- You need to add a specific, individual tool to your workflow
- The tool provides a single, focused function
- You want granular control over which tools are available to which agents
- You're building workflows with selective tool access for different agents
- You need one or a few specific tools from a server (use MCP Server for full collections)
Configuration Steps
Setting up an MCP Tool involves selecting the server source and choosing the specific tool you want to make available.
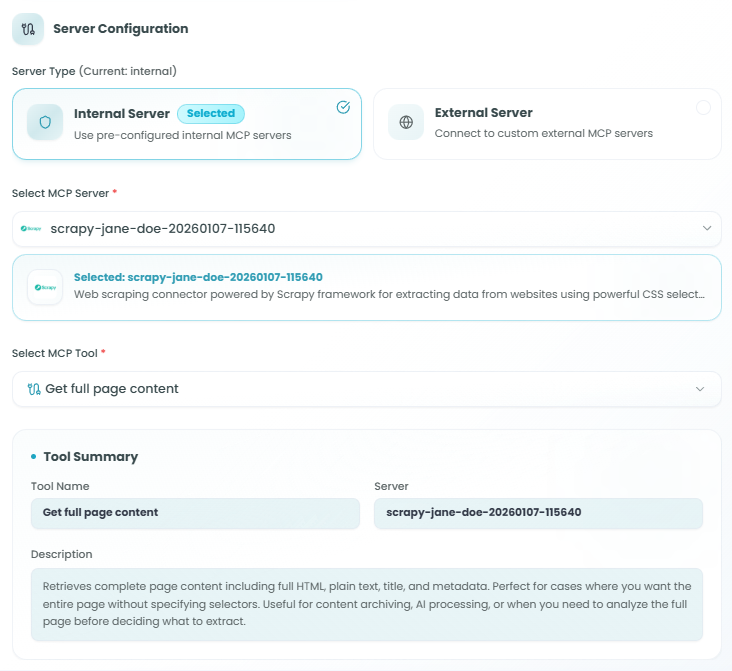
Step 1: Server Configuration
First, choose where your MCP tool will come from - either internal pre-configured servers or external custom servers.
Server Type:
Choose between two server types:
-
Internal Server (Recommended) - Use pre-configured internal MCP servers
- Ready-to-use servers provided by FlowGenX platform
- No additional configuration required
- Pre-tested and verified tools
- Managed authentication and credentials
- Ideal for most use cases
-
External Server - Connect to custom external MCP servers
- Connect to your own MCP server implementations
- Use third-party MCP servers
- Requires server URL and authentication configuration
- Useful for custom integrations and specialized tools
Step 2: Select MCP Server
After choosing the server type, select the specific MCP server that contains the tool you want to use.
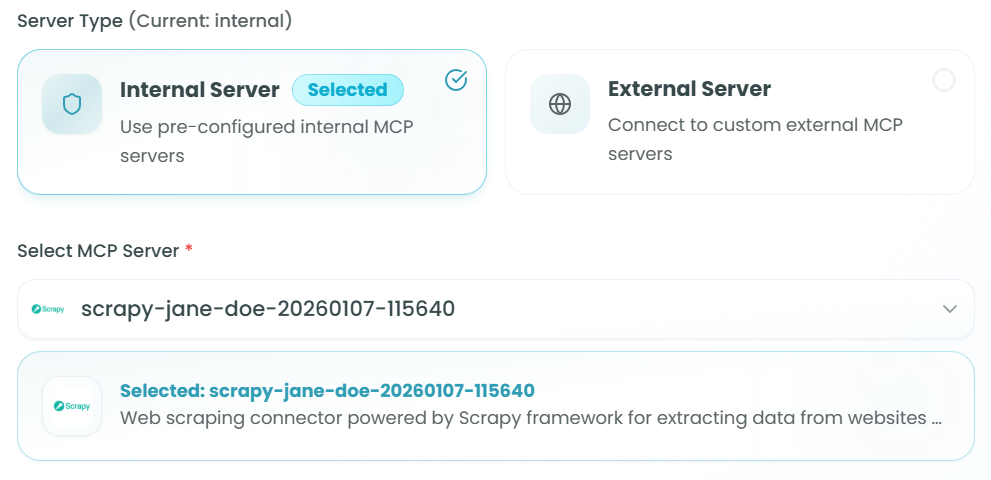
Selecting from Internal Servers:
- Click on the Select MCP Server dropdown
- Browse available internal MCP servers
- Each server displays:
- Server name and identifier
- Description of the server's purpose and capabilities
- Icon or logo for easy identification
Example Server:
- scrapy-jane-doe-20260107-115640
- Description: "Web scraping connector powered by Scrapy framework for extracting data from websites using powerful CSS selectors..."
- Provides tools for web scraping and content extraction
Once selected, the server information is displayed with its description, helping you understand what tools it provides.
Step 3: Select MCP Tool
After selecting a server, choose the specific tool from that server you want to configure.
- Click on the Select MCP Tool dropdown
- Browse available tools from the selected server
- View tool names and brief descriptions
- Select the tool that matches your workflow needs
Example Tool:
- Get full page content - Retrieves complete page content including HTML, text, title, and metadata
Step 4: Tool Summary
After selecting a tool, the Tool Summary section displays comprehensive information about the configured tool:
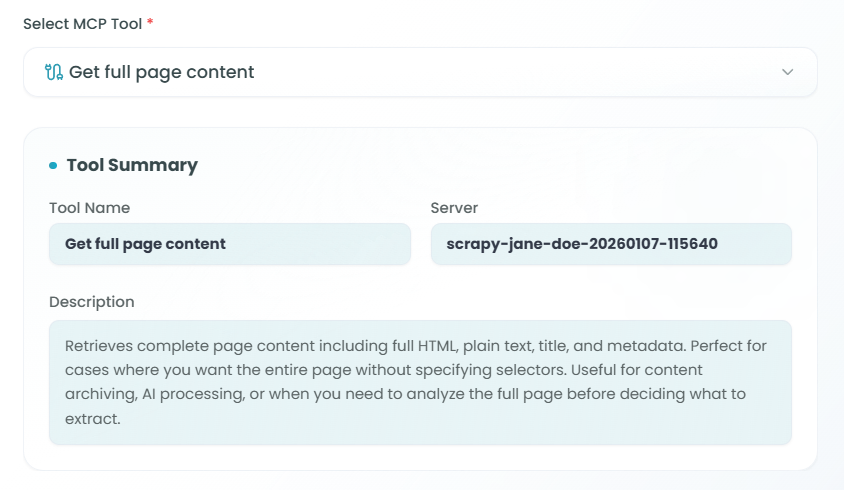
Tool Summary Information:
-
Tool Name - The name of the selected tool
- Example: "Get full page content"
-
Server - The MCP server providing this tool
- Example: "scrapy-jane-doe-20260107-115640"
-
Description - Detailed explanation of what the tool does
- Example: "Retrieves complete page content including full HTML, plain text, title, and metadata. Perfect for cases where you want the whole page without specifying selectors. Useful for content archiving, AI processing, or when you need to analyze the full page before deciding what to extract."
This summary helps you verify that you've selected the correct tool and understand exactly what it will do when invoked by an agent.
Connecting to Agents
Once configured, the MCP Tool node can be connected to agents in your workflow to make the tool available for their use.
Connecting to React Agent
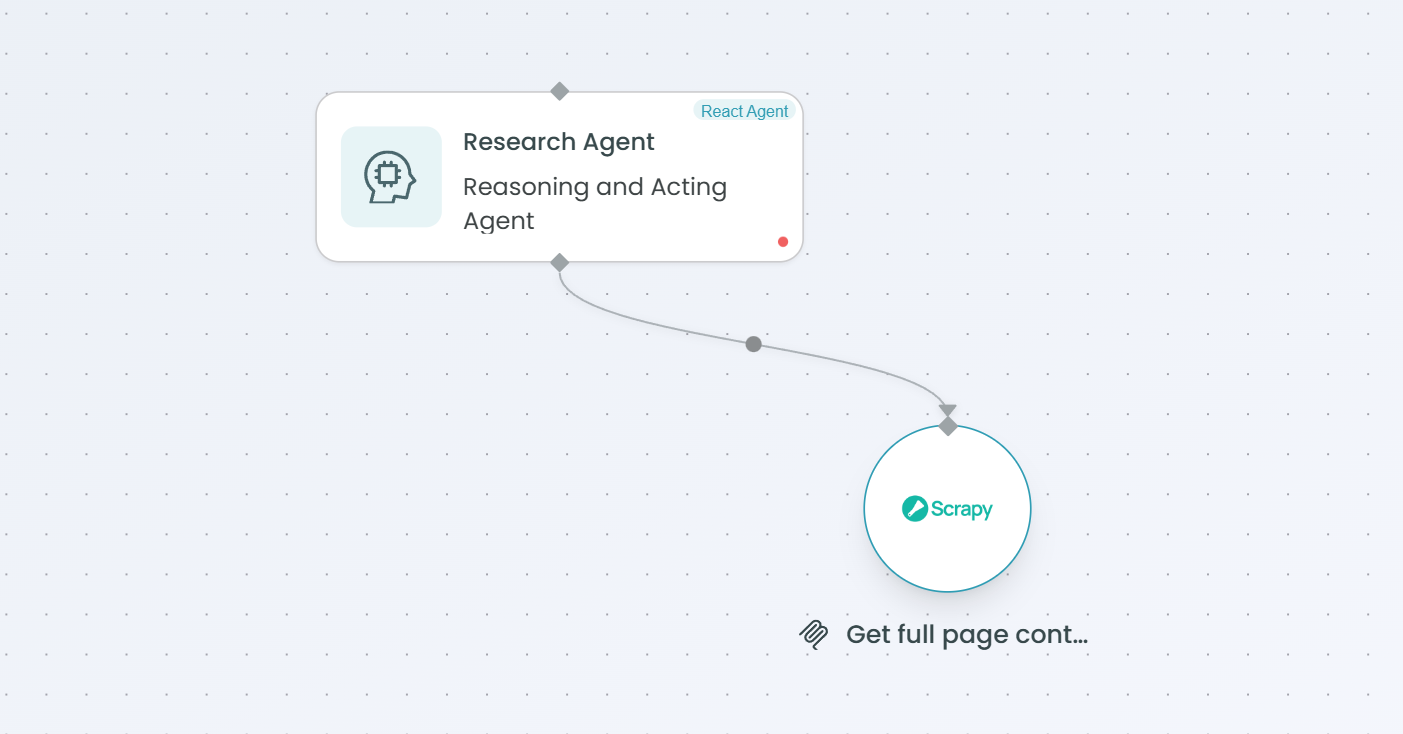
To connect the MCP Tool to a React Agent:
- Add both MCP Tool node and React Agent node to your workflow
- Draw a connection from the MCP Tool to the React Agent
- The React Agent will automatically detect the available tool
- Update the React Agent's prompt to explain when and how to use the tool
- The agent can now invoke the tool during execution
Benefits for React Agent:
- Single agent gains access to the specific tool
- Agent can use the tool as part of its task execution
- Tool results enhance the agent's capabilities
- Clear, focused tool availability
For detailed information on configuring React Agents, see the React Agent documentation.
Connecting to Supervisor Agent
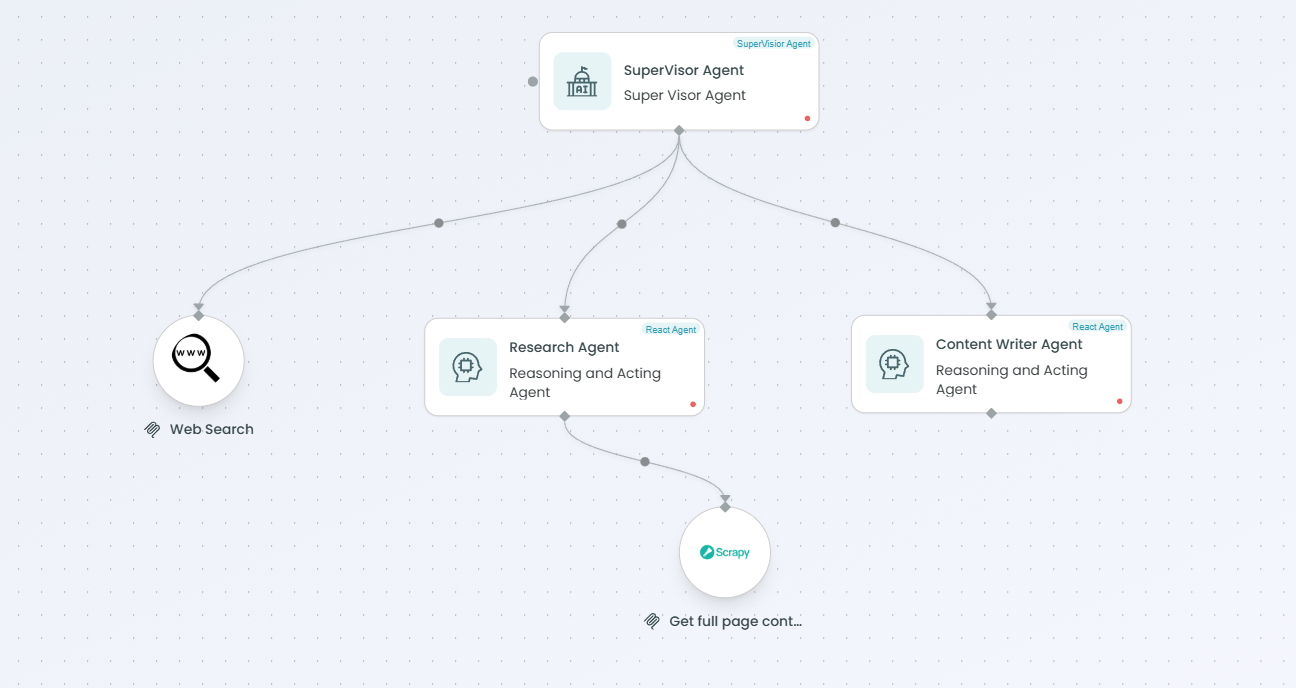
To connect the MCP Tool to a Supervisor Agent:
- Add both MCP Tool node and Supervisor Agent node to your workflow
- Draw a connection from the MCP Tool to the Supervisor Agent
- The Supervisor Agent will detect the tool and can delegate its use
- Update the Supervisor's prompt to explain the tool's purpose and when to use it
- The supervisor can invoke the tool directly or instruct child agents to use it
Benefits for Supervisor Agent:
- Supervisor can coordinate tool usage across multiple agents
- Tool can be used as part of complex orchestration strategies
- Supervisor can decide when and how to invoke the tool
- Enables intelligent tool delegation based on task requirements
For detailed information on configuring Supervisor Agents, see the Supervisor Agent documentation.
Using the MCP Tool in Your Workflow
After configuration and connection:
- The MCP Tool node appears in your workflow canvas
- Agents connected to the tool can discover and invoke it
- When an agent needs the tool's functionality, it can call it with appropriate parameters
- The tool executes its function (e.g., web scraping, API call, data processing)
- Results are returned to the agent for use in generating responses or making decisions
- The workflow continues with the enriched data from the tool
Tool Invocation Flow:
Agent receives task → Determines tool is needed →
Invokes MCP Tool with parameters →
Tool executes function →
Returns results to agent →
Agent processes results → Continues workflowBest Practices
Tool Selection
- Choose specific tools - Select only the tools you actually need for your workflow
- Understand tool capabilities - Read the tool description carefully before selection
- Match tools to tasks - Ensure the tool's function aligns with your workflow requirements
- Avoid redundancy - Don't add multiple tools that do the same thing
Server Selection
- Prefer internal servers - Use internal servers when available for easier management
- Verify server reliability - Ensure external servers are stable and available
- Check server documentation - Understand what tools each server provides
- Consider server maintenance - Internal servers are maintained by the platform
Agent Integration
- Document in prompts - Clearly explain the tool's purpose in your agent prompts
- Provide usage examples - Show agents when and how to use the tool
- Set clear boundaries - Define when the tool should and shouldn't be used
- Test thoroughly - Verify tool invocation works correctly before deployment
Tool Configuration
- Validate selections - Check the Tool Summary to confirm correct tool selection
- Review descriptions - Ensure you understand what the tool will do
- Test tool output - Verify the tool returns expected results
- Monitor usage - Track how often and how successfully the tool is being used
Common Use Cases
Web Scraping and Data Extraction:
- Connect web scraping tools to agents for content retrieval
- Extract structured data from websites
- Monitor web pages for changes
- Gather information for analysis or reporting
API Integration:
- Give agents access to external API calls
- Retrieve data from third-party services
- Send data to external systems
- Integrate with business applications
File Operations:
- Enable agents to read and write files
- Process documents and data files
- Generate reports and exports
- Manage file systems
Data Processing:
- Transform and enrich data
- Validate and clean datasets
- Perform calculations and analysis
- Format data for downstream use
Search and Retrieval:
- Search databases and knowledge bases
- Query external search engines
- Retrieve relevant information
- Find specific data points
Troubleshooting
Tool Not Available to Agent:
- Verify the MCP Tool node is connected to the agent node
- Check that the tool is properly configured
- Ensure the server is accessible and active
- Review agent logs for tool discovery issues
Tool Invocation Failing:
- Validate tool parameters are correct
- Check server connectivity and status
- Verify authentication and permissions
- Review tool-specific error messages
Unexpected Tool Results:
- Review the tool description to confirm expected behavior
- Check input parameters sent by the agent
- Validate the data being processed by the tool
- Test the tool independently to verify functionality
Agent Not Using Tool:
- Ensure the tool is mentioned in the agent's prompt
- Provide clear instructions on when to use the tool
- Add examples of tool usage to the prompt
- Check if the agent has other ways to accomplish the task
Monitoring Tool Usage
Monitor your MCP Tool performance:
- Track invocation frequency - How often agents are using the tool
- Measure success rates - Percentage of successful tool calls
- Monitor response times - How long tools take to execute
- Review tool outputs - Verify tools are returning useful results
- Analyze agent behavior - Understand when and why agents invoke tools
For more information on monitoring workflow executions, see the Traceability documentation.
MCP Tool vs MCP Server
Use MCP Tool when:
- You need one or a few specific tools
- You want granular control over tool access
- Different agents need different tools
- You're building focused, specialized workflows
Use MCP Server when:
- You need multiple tools from the same server
- You want to provide comprehensive toolsets
- All tools from a server are relevant to your workflow
- You prefer centralized tool management
For information on using MCP Servers, see the MCP Server documentation.
Next Steps
After setting up your MCP Tool:
- Connect the tool to your React Agent or Supervisor Agent
- Update agent prompts to explain the tool's purpose and usage
- Test tool invocation in the Playground
- Verify tool results are as expected
- Deploy your workflow with the integrated tool
- Monitor tool usage and performance
MCP Tools bring powerful external capabilities to your FlowGenX workflows, enabling agents to perform specialized tasks and integrate with external systems beyond their native language model capabilities.