Supervisor Agent
Coordinate and manage multiple agents in complex workflow orchestrations

The Supervisor Agent node enables coordination and management of multiple React Agents and tools within your workflows. Acting as an intelligent orchestrator, the Supervisor Agent delegates tasks to specialized child agents and tools, manages their execution, and synthesizes their outputs into cohesive results. This agent is powered by large language models (LLMs) to make intelligent decisions about task routing and delegation.
Why Use Supervisor Agent?
The Supervisor Agent is ideal when you need to:
- Orchestrate multi-agent workflows - Coordinate multiple specialized React Agents to handle complex tasks
- Delegate tasks intelligently - Route subtasks to the most appropriate agent based on capabilities
- Manage tool usage - Control and coordinate access to MCP tools and servers across your workflow
- Break down complex problems - Decompose large tasks into smaller subtasks handled by different agents
- Coordinate parallel execution - Manage multiple agents working simultaneously on different aspects of a task
- Synthesize results - Combine outputs from multiple agents and tools into unified responses
Supervisor Agent vs React Agent
Use Supervisor Agent when:
- You have multiple specialized agents that need coordination
- Tasks require decomposition into subtasks handled by different agents
- You need centralized control over agent delegation and tool usage
- Complex orchestration logic is required
Use React Agent when:
- A single agent can handle the entire task
- No delegation or coordination is needed
- The workflow is straightforward without multiple specialized steps
Configuration Steps
Setting up the Supervisor Agent involves the same 4 main configuration areas as the React Agent: Models, Prompts, Memory, and Schema. However, the Supervisor Agent adds coordination capabilities through connected agents and tools.

Step 1: Models Configuration
The Models tab for the Supervisor Agent works identically to the React Agent. You select and configure the AI model that will power the supervisor's decision-making and orchestration capabilities.
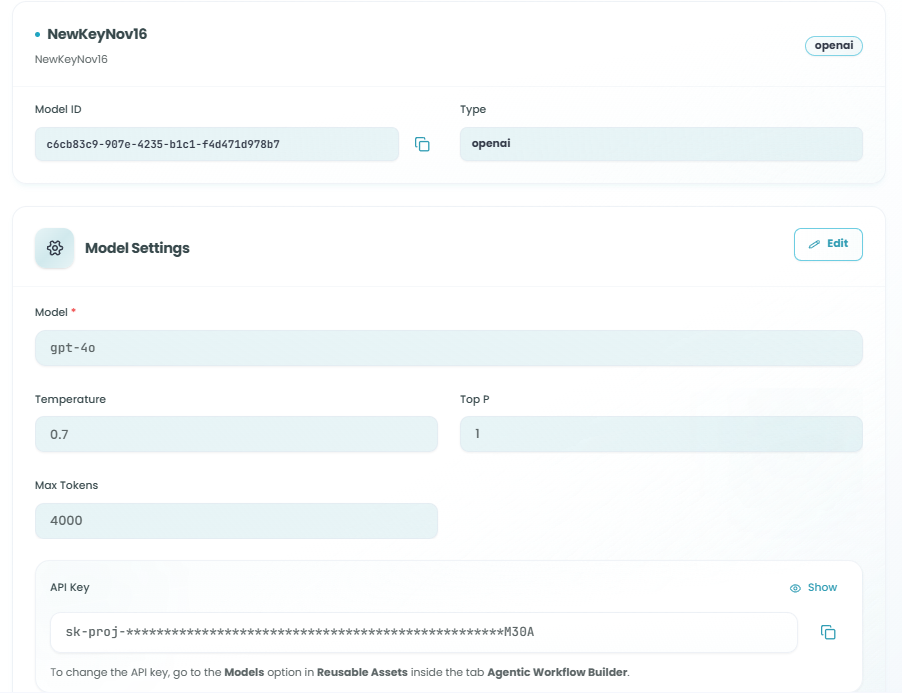
Model Configuration:
The Supervisor Agent uses the same model configuration as the React Agent:
- Click Select Model to choose an AI model
- Configure model settings:
- Model - The specific model version (e.g., gpt-4o, gpt-3.5-turbo)
- Temperature - Controls randomness (0.0 - 2.0)
- Top P - Controls diversity (0.0 - 1.0)
- Max Tokens - Maximum response length
- API Key - Authentication for the model provider
Model Selection for Supervisors:
For Supervisor Agents, consider:
- Use capable models - Supervisors need strong reasoning to delegate effectively
- Balance cost and performance - Supervisors make critical routing decisions
- Lower temperature - More consistent delegation decisions (typically 0.3 - 0.5)
For detailed information on model configuration, see the React Agent - Models Configuration documentation.
Step 2: Prompts Configuration
The Prompts tab for the Supervisor Agent is where you define the orchestration logic and delegation strategy. This is the most critical difference from the React Agent.
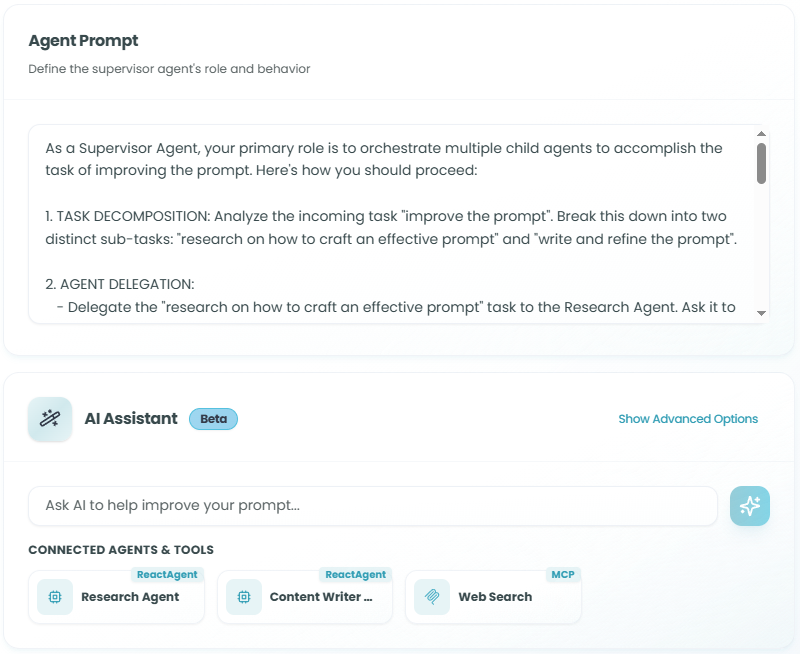
Agent Prompt:
The supervisor prompt should define:
- The supervisor's role and responsibilities
- How to analyze and decompose tasks
- When and how to delegate to child agents
- How to use available tools
- How to synthesize results from multiple agents
Writing Effective Supervisor Prompts:
Your supervisor prompt should clearly explain:
- Task Analysis - How to understand and break down incoming requests
- Delegation Strategy - When to use which child agent based on their specialties
- Tool Usage - How and when to use available MCP tools
- Result Synthesis - How to combine outputs from multiple agents
- Error Handling - What to do if an agent or tool fails
Example Supervisor Prompt:
You are a Supervisor Agent coordinating multiple specialized agents and tools.
Your responsibilities:
1. Analyze incoming requests and determine the best approach
2. Delegate tasks to appropriate child agents based on their expertise
3. Use tools when needed for specific operations
4. Coordinate parallel execution when tasks can run simultaneously
5. Synthesize results from all agents into a cohesive response
Connected Agents and their capabilities:
- {List of connected agents and what they do}
Available Tools:
- {List of available MCP tools and their functions}
When delegating:
- Choose the most appropriate agent for each subtask
- Provide clear instructions to child agents
- Wait for all required results before synthesizing
- Handle errors gracefully and retry if needed
Always explain your delegation strategy and how you're coordinating the agents.Connected Agents & Tools:
Below the prompt editor, you'll see the Connected Agents & Tools section displaying:
-
React Agents - Child React Agents connected to this supervisor
- Shows agent names and identifiers
- These are the agents the supervisor can delegate to
- Each agent has specialized capabilities defined in their own configuration
-
Generic Tools / MCP Tools - Tools available for the supervisor to use
- MCP Tool nodes connected to the workflow
- MCP Server nodes providing tool collections
- Functions and capabilities the supervisor can invoke
Prompt Best Practices for Supervisors:
- Be explicit about delegation - Clearly define when to use each child agent
- Document agent capabilities - Explain what each connected agent specializes in
- Define coordination logic - Specify how to manage multiple agents working together
- Set clear success criteria - Define what constitutes a successful delegation
- Include error recovery - Explain how to handle agent or tool failures
Variables and AI Assistant:
Like the React Agent, you can:
- Use
{{variable_name}}syntax for dynamic prompts - Leverage the AI Assistant to improve your supervisor prompts
- Use quick actions: Make it friendly, Be more concise, Add examples, More detailed
- Type custom improvement instructions in the AI Assistant
For detailed information on prompt features, see the React Agent - Prompts Configuration documentation.
Step 3: Memory Configuration
The Memory tab for the Supervisor Agent works identically to the React Agent, controlling how the supervisor remembers context across executions.
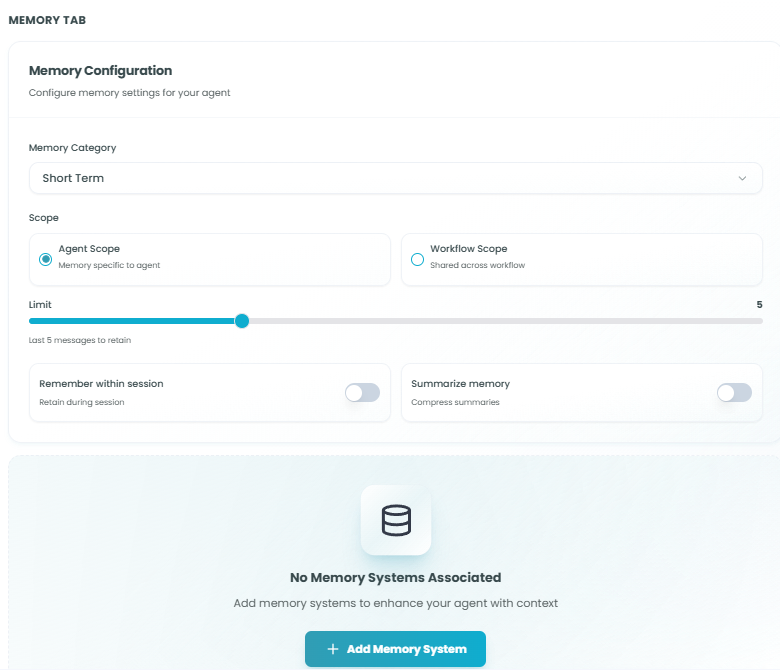
Memory Configuration:
Configure the same memory settings as React Agent:
- Memory Category - Short Term or Long Term
- Scope - Agent Scope (supervisor-only) or Workflow Scope (shared)
- Limit - Number of messages to retain
- Remember within session - Toggle for session persistence
- Summarize memory - Toggle for memory compression
- Associated Memory Systems - Redis, PostgreSQL, or other storage
Memory Considerations for Supervisors:
- Workflow Scope is powerful - Allows all child agents to share context
- Higher limits may be needed - Supervisors coordinate multiple interactions
- Summarization is valuable - Long delegation chains benefit from compression
- Consider persistence - Long-term memory helps supervisors learn delegation patterns
For detailed information on memory configuration, see the React Agent - Memory Configuration documentation.
Step 4: Schema Configuration
The Schema tab for the Supervisor Agent works identically to the React Agent, defining input and output data structures.
Schema Modes:
- Automatic IO - System infers schema from upstream nodes
- Manually Define - Full control over input and output fields
Schema Design for Supervisors:
- Input schema - Should capture all information needed for delegation decisions
- Output schema - Should accommodate synthesized results from multiple agents
- Consider aggregation - Output may combine data from multiple sources
- Plan for metadata - Include fields for delegation tracking and agent attribution
For detailed information on schema configuration, including Automatic IO, Manually Define mode, field creation, and expression usage, see the React Agent - Schema Configuration documentation.
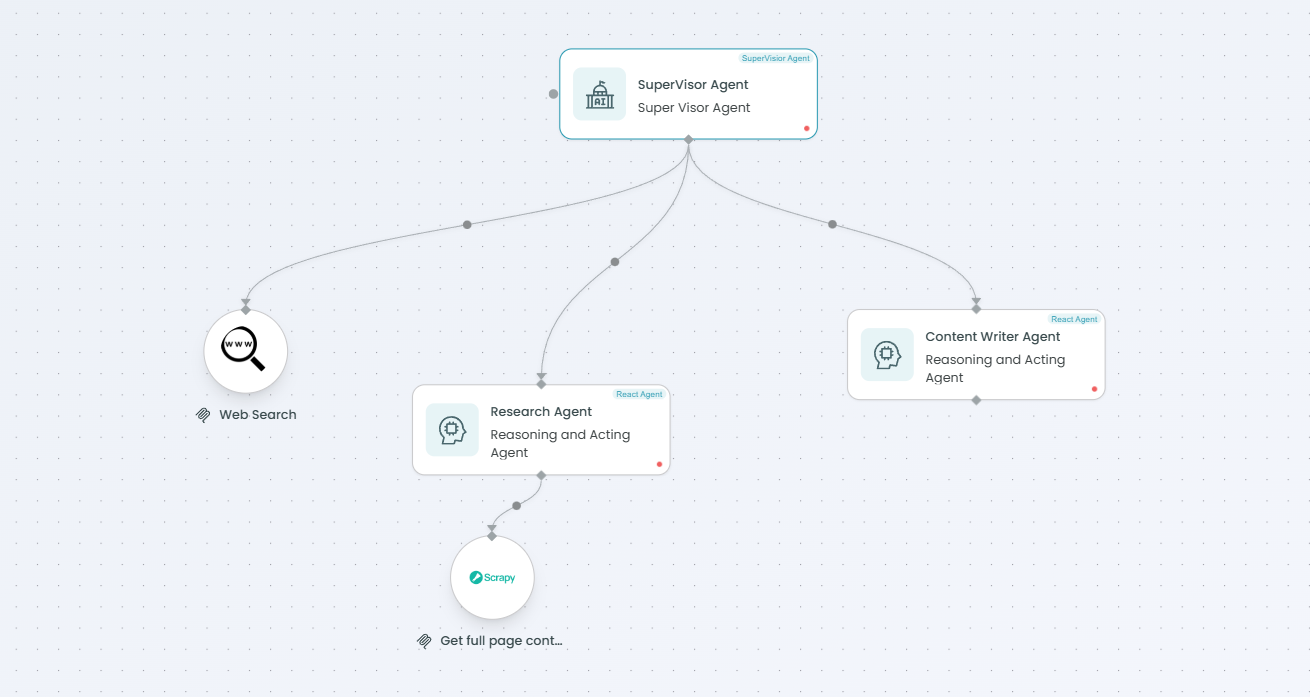
Connecting Child Agents and Tools
To build an effective supervisor workflow, you need to connect child agents and tools that the supervisor can delegate to.
Adding Child React Agents
- Add React Agent nodes to your workflow
- Configure each React Agent with specialized capabilities
- Connect them to the Supervisor Agent node
- The supervisor will automatically detect connected agents
- Update your supervisor prompt to explain each agent's role
Best Practices for Child Agents:
- Specialize each agent - Give each child agent a clear, focused responsibility
- Name agents descriptively - Use names that reflect their capabilities
- Document capabilities - Clearly describe what each agent can do in the supervisor prompt
- Avoid overlap - Minimize redundancy between child agents
- Test individually - Ensure each child agent works correctly before supervision
Adding MCP Tools and Servers
- Add MCP Tool or MCP Server nodes to your workflow
- Configure the tools with appropriate settings
- Connect them to the Supervisor Agent node
- The supervisor will automatically detect available tools
- Update your supervisor prompt to explain when to use each tool
MCP Integration:
The Supervisor Agent can coordinate usage of:
- MCP Tool Nodes - Individual tools for specific functions
- MCP Server Nodes - Collections of related tools from MCP servers
For detailed information on configuring MCP integration, see:
- MCP Tool Node documentation
- MCP Server Node documentation
Using the Supervisor Agent in Your Workflow
After configuration is complete:
- The Supervisor Agent receives input based on your schema definition
- The supervisor analyzes the task using its configured prompt
- The supervisor makes delegation decisions based on available child agents and tools
- Child agents execute their delegated tasks
- Tools are invoked as needed for specific operations
- The supervisor synthesizes results from all delegated tasks
- Output is structured according to your schema definition
- Downstream nodes receive the supervisor's synthesized output
Delegation Flow:
Input → Supervisor Analysis → Task Decomposition →
Delegate to Child Agents + Use Tools →
Collect Results → Synthesize → OutputBest Practices
Supervisor Prompt Engineering
- Define clear roles - Explicitly state the supervisor's responsibilities
- Document all agents - List each child agent and their capabilities
- Explain delegation logic - Provide clear criteria for routing decisions
- Set coordination rules - Define how agents should work together
- Include examples - Show sample delegation scenarios
- Plan for edge cases - Handle situations where no agent is appropriate
Child Agent Design
- Single responsibility - Each child agent should have one clear purpose
- Complementary capabilities - Design agents to cover different aspects of the problem space
- Clear interfaces - Define explicit input/output contracts for each agent
- Independent operation - Child agents should work without depending on each other
- Error resilience - Each agent should handle its own errors gracefully
Delegation Strategy
- Analyze before delegating - Understand the full task before breaking it down
- Parallel when possible - Delegate independent subtasks simultaneously
- Sequential when needed - Respect dependencies between subtasks
- Monitor progress - Track which agents are working on what
- Synthesize intelligently - Combine results in a meaningful way
Performance Optimization
- Minimize delegation overhead - Don't delegate unnecessarily simple tasks
- Reuse results - Cache outcomes from child agents when appropriate
- Limit delegation depth - Avoid deeply nested supervisor chains
- Monitor costs - Each delegation incurs additional model API calls
- Batch when possible - Group similar tasks for single agent execution
Common Use Cases
Complex Document Processing:
- Supervisor analyzes document type
- Delegates extraction to specialized agents (tables, text, images)
- Uses tools for format conversion
- Synthesizes complete document analysis
Multi-Step Research:
- Supervisor breaks research query into topics
- Delegates each topic to research agents
- Uses MCP tools for web search and data retrieval
- Combines findings into comprehensive report
Customer Support Automation:
- Supervisor classifies customer inquiry
- Delegates to specialized agents (billing, technical, general)
- Uses tools to access customer data and knowledge base
- Synthesizes personalized response
Data Pipeline Orchestration:
- Supervisor coordinates data processing stages
- Delegates validation, transformation, enrichment to agents
- Uses tools for data quality checks
- Produces final processed dataset
Multi-Agent Collaboration:
- Supervisor manages team of specialized agents
- Coordinates agent interactions and data sharing
- Resolves conflicts between agent outputs
- Delivers unified solution
Troubleshooting
Supervisor Not Delegating:
- Verify child agents and tools are properly connected
- Check supervisor prompt clearly explains when to delegate
- Ensure delegation criteria are not too restrictive
- Review logs to see supervisor's reasoning
Poor Delegation Decisions:
- Refine supervisor prompt with clearer agent descriptions
- Lower temperature for more consistent decisions
- Add delegation examples to the prompt
- Test child agents individually to verify capabilities
Results Not Synthesizing:
- Check that supervisor prompt explains synthesis process
- Verify output schema can accommodate combined results
- Ensure all delegated tasks are completing successfully
- Review memory settings for context retention
Performance Issues:
- Reduce unnecessary delegation
- Optimize child agent configurations
- Consider parallel execution for independent tasks
- Monitor token usage across all agents
Child Agent Errors:
- Implement error handling in supervisor prompt
- Configure retry logic for failed delegations
- Add fallback strategies when agents fail
- Monitor individual agent performance
Monitoring Multi-Agent Workflows
Monitor your Supervisor Agent and child agents:
- Track delegation patterns - Understand which agents are used most frequently
- Measure synthesis quality - Evaluate how well results are combined
- Monitor costs - Track API usage across supervisor and all child agents
- Analyze performance - Identify bottlenecks in the delegation chain
- Review agent interactions - Understand how agents collaborate
- Test edge cases - Verify handling of unusual delegation scenarios
For more information on monitoring workflow executions, see the Traceability documentation.
Next Steps
After setting up your Supervisor Agent:
- Configure and test each child agent individually
- Set up MCP tools and servers the supervisor will use
- Write a comprehensive supervisor prompt with delegation logic
- Test the full multi-agent workflow in the Playground
- Refine delegation criteria based on test results
- Monitor real-world performance and iterate
- Optimize for cost and latency
The Supervisor Agent enables sophisticated multi-agent orchestration in FlowGenX workflows, allowing you to build complex, intelligent systems that coordinate specialized agents and tools to solve challenging problems that would be difficult or impossible for a single agent to handle alone.